The inverted yield curve has long been one of the most reliable predictors of economic downturns, concerning investors and economists. It is a situation where the yield on a short-term debt instrument, such as a Treasury bill, is higher than that of a long-term debt instrument, such as a Treasury bond. Usually, under normal circumstances, investors demand a higher yield for lending money for a longer period.
In this article, we will discuss inverted yield curve, explore its implications, and understand why it is an important indicator of economic uncertainty.
What is the Yield Curve?
The yield curve is a graphical representation of the relation between interest rates and the maturity periods of fixed-income assets, especially government bonds. In a normal yield curve, longer-term bonds carry higher interest rates than shorter-term bonds, reflecting the expectation of future economic growth and inflation. However, in some circumstances, the yield curve might invert, with short-term bonds yielding more than long-term bonds.
Causes of an Inverted Yield Curve:
As we know, the Inverted Yield Curve occurs when short-term interest rates exceed long-term rates, creating an abnormal shape in the yield curve. The market’s anticipation of an economic slowdown or recession sometimes leads to an inverted yield curve. When investors anticipate future economic weakness, they tend to seek the safety of longer-term bonds, driving up their prices and consequently pushing down their yields.
Another possibility is that the Central Bank is raising interest rates to combat inflation. When the Fed or any other central bank raises interest rates, it becomes more expensive for businesses and consumers to borrow money. This can slow economic growth.
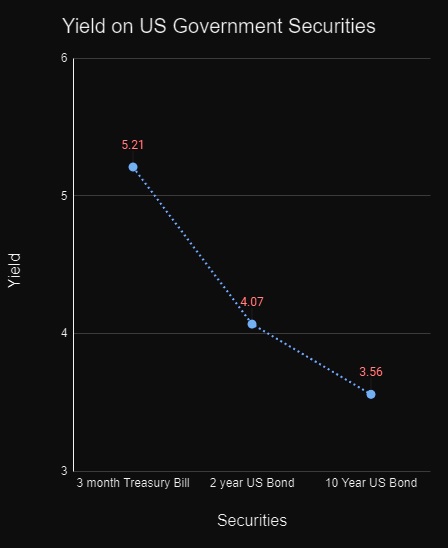
As of May 16, 2023, the interest rates on the 3-month Treasury bill, 2-year US bond, and 10-year US bond are 5.21%, 4.07%, and 3.56% respectively, a perfect depiction of an inverted yield curve.
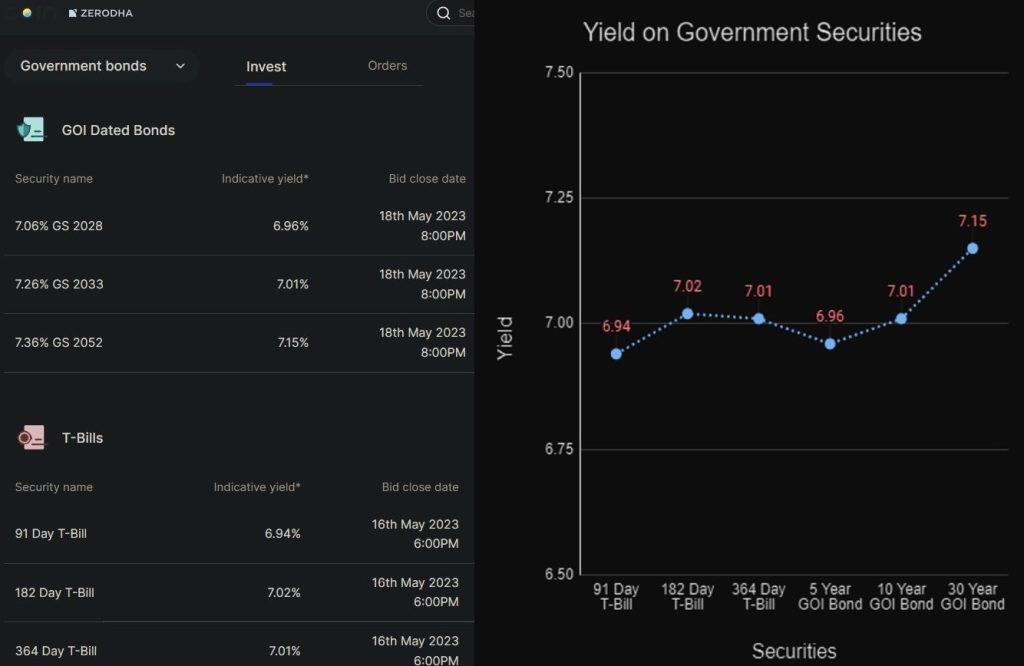
We have also been experiening a mild inverted yield curve in India for the past few months. I’ve charted the interest rates of various government securities for reference. There is a clear inversion in the yields on 182 Day T-Bill to 5 Year Government Bond.
Why is an Inverted Yield Curve a sign of recession?
Historically, inverted yield curve has been used for predicting the economic recessions. This relationship has held strong for several decades and closely monitored by economists, investors, and policymakers. An inverted yield curve has preceded nearly all major recessions in the United States over the past 50 years, including the 2008 financial crisis and the dot-com bubble burst in 2001.
The inversion of the yield curve implies a loss of confidence in the economy’s prospects. It suggests that investors are ready to accept lower yields on longer-term bonds due to their lack of confidence in the short-term economic outlook. The banks’ ability to lend profitably is weakened, as their borrowing costs rise relative to the interest rates they receive on loans. This tightening of credit can have adverse effects on consumer and business spending, potentially leading to an economic downturn.
Limitations of this Inference:
While the inverted yield curve has historically been an excellent predictor, some experts argue that the current economic landscape may have limited its forecasting power. Unconventional monetary policy initiatives, such as quantitative easing, have skewed the bond market and reduced the reliability of historical correlations. Additionally, structural changes in the global economy, such as increased capital flows and globalization, might have altered the yield curve’s predictive capabilities.
It is essential to view it as one among many indicators than relying solely on it for anticipating economic downturns. Other factors, such as labor market conditions, consumer sentiment, and fiscal policy decisions, should be considered along with the yield curve to form a comprehensive economic analysis.
What does an Inverted Yield Curve mean for Investors?
An inverted yield curve can be a sign of trouble ahead for the economy. However, it is important to remember that the yield curve is not always an accurate predictor of recessions. If you are an investor, it is important to monitor and be aware of the risks. If you are concerned about the possibility of a recession, you may want to consider adjusting your investment portfolio to reduce your risk.
Here are some tips for investors:
- Increase your cash reserves. Having a healthy cash reserve that pays for at least one year of household expenses can help you weather a recession.
- Reduce your exposure to risky assets. Consider selling some of your overvalued stocks and investing in shorter-term debt instruments like T-bills.
- Investing in defensive assets like bonds and gold can help preserve your portfolio from losses during a downturn.
- Diversifying your portfolio helps you in minimizing the risk.
Conclusion:
The inverted yield curve is a valuable tool for economists and investors in assessing the state of the economy and identifying potential risks. Even though it is not foolproof and has limitations, its historical accuracy in predicting recessions should not be overlooked. The recent debates and attention have underlined its importance as an early warning indicator for a financial crisis. Understanding the implications and limitations of complex financial landscapes can help us make educated decisions and mitigate risks in an ever-changing economic panorama..
Disclaimer:
I provide the information and my views on the website only to educate new investors and stock market enthusiasts on equity and other market investments. Please consult a registered financial advisor before making any investments in the stock or commodity markets. In case of any queries, you can contact me on Contact Form or email: admin@valueinvestingonline.in.




