Silver has always been one of the popular investments among both novice and experienced investors. Its dual existence as a precious metal and an industrial commodity provides it with distinct properties that attract investors of all classes. Currently, it is priced around $31.5 for an ounce on LBMA. While frequently overshadowed by gold, silver has its own characteristics that make it an appealing addition to a well-diversified investment portfolio.
Why Invest in Silver?
Hedge against inflation:
Similar to gold, silver is also viewed as a safe-haven asset, particularly during periods of inflation or economic turmoil. Fiat currencies tend to lose purchasing power over time, and precious metals such as gold, silver, and platinum retain their value and provide hedge against the depreciation of paper money.
Diversification:
Diversification involves investing across several asset classes to decrease risk of losing investment value. Silver offers diversity beyond standard investments such as equities and bonds. Its price does not track major financial markets thus providing a possible safety net during downturns.
Affordability:
Compared to gold, one of the most significant advantages of silver is its low cost. While gold prices have already reached levels almost unattainable for many small investors, silver provides a more affordable starting point for precious metal investments. Investors may purchase bigger quantities of silver for the same price as a small amount of gold.
Industrial Demand:
Contrary to gold, which is largely used for investment and ornament, silver also has several industrial uses. It is widely utilized in electronics, solar panels, medical equipment, and other applications. This simultaneous demand from both investors and industry provides a solid foundation for silver’s long-term price increase.
Historical Significance:
Silver had been used as currency for thousands of years and served as a store of value throughout cultures. Even though it is no longer utilized in everyday transactions, silver is a storage of value among various communities.
Investing in Silver:
There are two main ways to invest in silver.
Physical Silver: Many investors like to own physical silver in the form of coins or bars. American Silver Eagle and Canadian Silver Maple Leaf are the most popular options. In India, MMTC PAMP and BPRL are well-known brands for gold and silver coins and bars. While investing in physical silver gives investors direct control over their investment, it also comes with additional costs like insurance and security storage.
Silver Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs): For those who do not prefer physical silver, investing in silver ETFs provides a convenient way to gain exposure to silver prices without owning physical silver. These ETFs are actively traded on stock markets, and their value directly reflects the cost of silver. One of the most well-known silver ETFs is the iShares Silver Trust (SLV). SILVERBEES, SILVERIETF, and SILVER are silver ETFs traded in the Indian stock markets.
Other options:
Investing in silver can also be done in other ways.
One such option is to buy stocks in companies that mine or process the metal. These stocks can be more volatile than the actual price of silver since they are affected by both silver prices and company-specific risks. Investors comfortable taking more risks invest in silver mining stocks for higher profits. Pan American Silver Corp, Wheaton Precious Metals Corp are some of the publicly traded companies. Currently, HINDZINC is the only public traded company that is in the business of mining silver in India.
Experienced investors trade silver futures contracts or options. These financial derivatives allow investors to bet on the future price of silver, offering the potential for significant returns. However, there is a high level of risk due to leverage. These investment options are not recommended for beginners due to their complexity and risk profile.
Advancement of blockchain technology has led to the emergence of silver-backed cryptocurrencies in recent years. These digital assets are linked to the price of silver and offer a new way for tech-savvy investors to gain exposure to the metal without physical ownership or relying on traditional markets.
Risks associated with investing in Silver:
Price Volatility:
Investing in silver carries risks, including price volatility that can cause significant fluctuations over short periods. This volatility is influenced by factors such as industry demand, economic conditions, derivatives trading, and changes in market sentiment. Investors should be prepared themselves for high volatility and consider silver as a long-term investment.
Storage and Security:
Those who invest in physical silver face challenges in storing and preserving the metal. A secure storage solution is necessary, whether it is a personal safe or a professional vault service. Insurance costs also add to the overall expense of owning physical silver.
Market Liquidity:
Even though it is traded internationally, silver has a smaller and less liquid market compared to gold. Sometimes this might lead to larger price spreads and less efficient trading, especially for high-volume transactions. This is not a big concern since Silver is the most actively traded commodity after gold in precious metals.
Industrial Dependency:
Since industries consume a significant portion of the global silver supply, the metal is vulnerable to economic fluctuations. During a global downturn, when sectors decrease production, silver demand may decline, resulting in the lower prices.
Gold vs Silver:
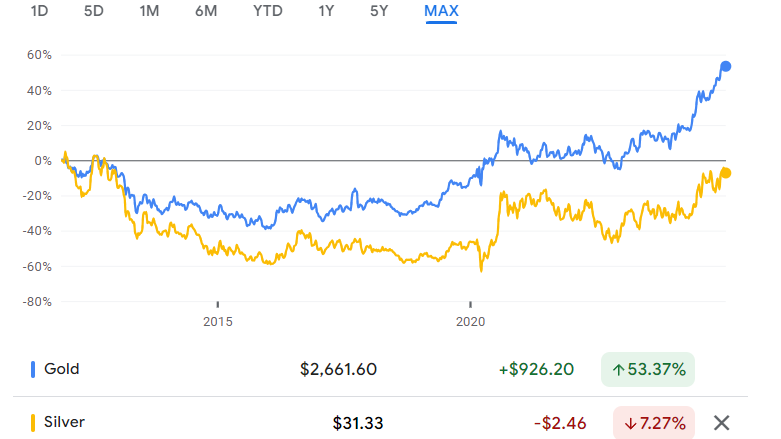
Silver and gold are often associated with investments in precious metals, but they have distinct qualities. Gold is primarily considered an investment and a store of wealth, while silver serves as both an investment and an industrial commodity. Over time, the gold-to-silver ratio, which represents the amount of silver needed to purchase one ounce of gold, has fluctuated. Some investors use this ratio to determine whether to buy or sell silver in comparison to gold. According to this, it is a signal to buy silver if the ratio is over 80.
The current gold-to-silver ratio is around 85. This ratio was 20 in 1979. In the last 12 years, Gold has outperformed Silver by a significant margin. Gold is up 53%, whereas silver is down 7.2%. However, it seems like silver is catching up with gold; both of these precious metals are up 78% in the last 5 years. Silver appears to be bullish on the charts over the short to mid-term. With gold rising very fast, even if the gold-to-silver ratio falls to 80, we could soon witness $50 an ounce Silver.
Conclusion:
Silver’s dual role as a precious metal and an industrial commodity offers investors a unique opportunity. It can act as a hedge against inflation, diversify portfolios, and provide potential for growth due to its industrial demand. However, silver’s price volatility, storage challenges, and sensitivity to economic conditions should also be considered.
Silver is a great option for those seeking a more affordable alternative to gold that offers a tangible asset. Silver provides various ways to participate in the market, including owning physical silver, investing in ETFs, buying mining stocks, and trading derivatives. It’s well-suited for long-term investors who can tolerate market fluctuations and are looking to make a wise addition to their investment portfolios.
Disclaimer:
I provide the information and my views on the website only to educate new investors and stock market enthusiasts on equity and other market investments. Please consult a SEBI registered financial advisor before making any investments in the stock or commodity markets. In case of any queries, you can contact me on Contact Form or email: admin@valueinvestingonline.in.